There are at least more than 1 million species of insects in the world that can be used as feed protein raw materials. Our common black soldier fly has four major advantages and has broad utilization prospects. Analysis of the advantages of black soldier fly replacing fish meal
Global insects are hailed as the last piece of cake given to mankind by God.In recent years, the insect protein industry has gradually emerged and become a new favorite in the fields of agriculture, animal husbandry and food. Experts analyze the differences and connections between insect protein and fishmeal protein. Fishmeal, an important source of protein feed for livestock and poultry, is mainly produced in South American countries.In recent years, due to unreasonable fishing and the impact of natural disasters, the production of fishmeal has been declining year by year, and the price has been rising.The cost of feeding fishmeal as the main protein feed is getting higher and higher.For this reason, people have been working hard to find new animal protein resources.As a variety, large number, and nutritious protein resource, insects are increasingly valued by people and have become the targets of people's development and utilization.1. Insects are animal protein feeds with greater development potential. Insects are a group of animals with more species and more individuals on the earth today. Among the 1.5 million species of organisms officially named and described by scientists, there are more than 900,000 species of insects. , and American entomologists believe after years of research that there are more than 10 million insect species in the world.Chinese entomologists initially estimate that there are about 1.5 million insect species in the country.Insects not only have many types, but also have large colonies and very strong reproductive capabilities.For example, a pair of flies can breed 200 billion maggots in four months and accumulate more than 600 tons of pure protein.It usually only takes 1 to 11 days for fly maggots to develop into adults, and only 45 days from eggs to adult maggots. Its short cycle, rapid reproduction, and high yield are unmatched by many other organisms. The newly hatched larvae is 0.08 mg. , under appropriate temperatures, after 4 to 5 days of growth, the weight of the maggots can reach 20 to 25 mg, and the total biomass increases 25 to 350 times.As lower animals, insects' assimilation efficiency in the energy conversion of ecosystems is about half that of mammals, but their production efficiency is 15 to 40 times that of mammals, which is unmatched by other methods of protein production.A termite queen can produce 480 to 900 eggs per day, and the number of eggs laid per year
 reaches hundreds of thousands. Some queens in the order Hymenoptera can lay 2,000 to 3,000 eggs per day, and nearly one million eggs per year. Eggs.2. Insects have high nutritional value. According to experts, insects have high nutritional value. According to domestic and foreign studies, insects not only have high protein content, but also have a very reasonable amino acid ratio in the protein.As one of the comparative methods of protein nutritional value, it is commonly evaluated by the ratio of essential amino acid content (E) to the total amount of amino acids (N+E) in the sample.The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and the World Health Organization propose that essential amino acids in the sample account for about 40% of the total amino acids and have ideal nutritional value.The proportion of amino acids contained in insects is close to the amino acid proportion model established by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.In recent years, the results of analysis and measurement of dozens of insects show that the protein content of different insects ranges from 13.5% to 61.8% for adults; 19.4% to 72.5% for larvae; and 46.1% to 85.3% for pupae.The digestibility of insect protein is also close to or exceeds the digestibility of high-quality protein, which shows that insect protein can be used as a high-quality protein feed for poultry.In today's fishmeal shortage, using insect protein as animal protein instead of fishmeal has become the direction of many countries to solve the problem of animal protein feed sources.3. Raising insects can reduce pollution. my country’s poultry and livestock breeding industry is moving towards large-scale development.Industrial development is currently mostly concentrated in the suburbs. The scale of breeding farms is getting larger and larger, and there are more and more poultry and livestock manure. Pollution is becoming increasingly prominent, which has become a major problem for environmental protection.It is estimated that poultry and livestock discharge 1.367 billion tons of wet manure annually across the country.Such a huge amount of livestock manure, if not utilized, will cause serious pollution to the environment, and rational utilization will be a considerable resource and wealth. It can be seen that the significance and potential of developing and utilizing livestock manure is huge.Detritivorous insects account for 17.3% of the total number of insects. They keep the environment clean by decomposing animals, plants and excrement, and at the same time realize material recycling.Coprophagous insects such as house flies can effectively handle livestock manure and have high ecological and economic benefits.The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan has organized and implemented an insect utilization industry development plan since 1993. The research project of Tanaka Engineering Co., Ltd. is "Using insects to process poultry excrement and production of feeding insects", that is, using flies and coprophagous insects As an object, develop and systematize a large number of value-added methods to process poultry excrement and use the breeding insects as feed for poultry production.4. Development status of insect feed Since the 1960s, countries around the world have taken solving the protein problem as the main direction of developing feed resources. Artificially raising insects as feed is an important topic of development and research.The United States, the former Soviet Union, West Germany, North Korea and Hungary and other countries have successively carried out experimental research on using feces to raise maggots. In the late 1970s, some scientific research units in our country re-launched research in this area. At present, house flies, silkworm chrysalis, flies Maggots and mealworms have been well developed and utilized as protein feeds, and some have even been produced on an industrial scale.The development of feed insects is an important way for my country to solve the shortage of animal protein, and it will definitely develop greatly in the future.To this end, several issues should be paid attention to in the process of strengthening research: First, there are many types of insects with complex living habits. How to further develop and utilize species with more economic value.The second is to conduct extensive research on feed insect bait and develop feed resources that are low-cost, widely sourced, and suitable for the growth and development of feed insects.5. Effects of black soldier fly larvae meal replacing fish meal on the growth performance, body composition, serum biochemical indicators and antioxidant capacity of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei 1710242274484900.jpg Fish meal is the most important high-quality animal protein raw material for aquatic animals, with high protein content It has the characteristics of high content, balanced amino acids, rich unsaturated fatty acids, no anti-nutritional factors and easy digestion and absorption. It is widely used in carnivorous or omnivorous aquatic animal feeds.With the rapid development of my country's aquaculture industry, the demand for fishmeal has been increasing in recent years. However, long-term overfishing of marine fisheries has led to a shortage of fishery resources. Fishmeal production has been decreasing year by year, and the raw material market has been in short supply, causing prices to continue to rise.The high price of fishmeal has resulted in high feed costs, which has seriously restricted the sustainable development of the aquaculture industry.Therefore, seeking healthy, safe, resource-rich and cheap protein alternative sources has become one of the effective ways to solve the fishmeal shortage problem.The black soldier fly (Hermitiallucens), also known as the bright-spotted water fly, is an insect belonging to the family Diptera. The larval stage can efficiently convert organic matter such as livestock and poultry manure, household food waste, etc. into its own nutrients. It has It has the characteristics of strong fecundity, wide adaptability, large biomass, easy processing and comprehensive nutrition.Black soldier fly larvae meal (BSFLM) is a dry insect meal obtained by screening, drying and crushing the black soldier fly larvae stage. Due to the consumption of waste from different sources, the nutritional content of black soldier fly larvae powder There are certain differences. Generally, the dry matter of insect meal contains 35% to 45% crude protein and 10% to 40% crude fat. The essential amino acid pattern is similar to that of fish meal. It has broad application prospects as animal feed.Studies have shown that black soldier fly larvae powder replaces part of the fish meal in feed, and has achieved good application results in rainbow trout, sea bass, yellow catfish, Jian carp, koi and turbot.Litopenaeus vannamei, also known as White Penaeus vannamei, has the characteristics of fast growth, wide breeding distribution and high nutritional value. It is the shrimp breeding species with the largest breeding area and annual output in the world and in my country.Research shows that the apparent digestibility of black soldier fly larvae powder (crude fat content up to 37.0%) by Litopenaeus vannamei in dry matter and crude protein is both above 82%, and it is found in high salt (30.7‰) Under breeding conditions, black soldier fly larvae meal (crude fat content: 15.1%) can partially replace fish meal without affecting the growth and body composition of Litopenaeus vannamei.Litopenaeus vannamei is an euryhaline species and one of the few shrimp species that can tolerate low salt. Therefore, fishmeal substitutes are added to the feed to study its effects on the growth performance, body composition, and body composition of Litopenaeus vannamei under low-salt conditions. The impact of serum biochemical indicators and antioxidant capacity has practical significance.6. Materials and Methods 6.1 The test feed uses fish meal (crude protein content: 73.7%, crude fat content: 7.9%), soybean meal, and peanut meal as the main protein sources, high-gluten flour as the main sugar source, and fish oil and phospholipid oil as the main fats. Prepare the basal feed (G0, as a control) from the source, and then replace 10% (G10), 15% (G15), 20% (G20), 25% (G25), 30% (G30) of the basal feed with black soldier fly larvae powder. ) is used to prepare 5 kinds of feeds with fish meal. The data analysis chart of the composition and nutritional level of 6 kinds of test feeds is as follows
reaches hundreds of thousands. Some queens in the order Hymenoptera can lay 2,000 to 3,000 eggs per day, and nearly one million eggs per year. Eggs.2. Insects have high nutritional value. According to experts, insects have high nutritional value. According to domestic and foreign studies, insects not only have high protein content, but also have a very reasonable amino acid ratio in the protein.As one of the comparative methods of protein nutritional value, it is commonly evaluated by the ratio of essential amino acid content (E) to the total amount of amino acids (N+E) in the sample.The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and the World Health Organization propose that essential amino acids in the sample account for about 40% of the total amino acids and have ideal nutritional value.The proportion of amino acids contained in insects is close to the amino acid proportion model established by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.In recent years, the results of analysis and measurement of dozens of insects show that the protein content of different insects ranges from 13.5% to 61.8% for adults; 19.4% to 72.5% for larvae; and 46.1% to 85.3% for pupae.The digestibility of insect protein is also close to or exceeds the digestibility of high-quality protein, which shows that insect protein can be used as a high-quality protein feed for poultry.In today's fishmeal shortage, using insect protein as animal protein instead of fishmeal has become the direction of many countries to solve the problem of animal protein feed sources.3. Raising insects can reduce pollution. my country’s poultry and livestock breeding industry is moving towards large-scale development.Industrial development is currently mostly concentrated in the suburbs. The scale of breeding farms is getting larger and larger, and there are more and more poultry and livestock manure. Pollution is becoming increasingly prominent, which has become a major problem for environmental protection.It is estimated that poultry and livestock discharge 1.367 billion tons of wet manure annually across the country.Such a huge amount of livestock manure, if not utilized, will cause serious pollution to the environment, and rational utilization will be a considerable resource and wealth. It can be seen that the significance and potential of developing and utilizing livestock manure is huge.Detritivorous insects account for 17.3% of the total number of insects. They keep the environment clean by decomposing animals, plants and excrement, and at the same time realize material recycling.Coprophagous insects such as house flies can effectively handle livestock manure and have high ecological and economic benefits.The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan has organized and implemented an insect utilization industry development plan since 1993. The research project of Tanaka Engineering Co., Ltd. is "Using insects to process poultry excrement and production of feeding insects", that is, using flies and coprophagous insects As an object, develop and systematize a large number of value-added methods to process poultry excrement and use the breeding insects as feed for poultry production.4. Development status of insect feed Since the 1960s, countries around the world have taken solving the protein problem as the main direction of developing feed resources. Artificially raising insects as feed is an important topic of development and research.The United States, the former Soviet Union, West Germany, North Korea and Hungary and other countries have successively carried out experimental research on using feces to raise maggots. In the late 1970s, some scientific research units in our country re-launched research in this area. At present, house flies, silkworm chrysalis, flies Maggots and mealworms have been well developed and utilized as protein feeds, and some have even been produced on an industrial scale.The development of feed insects is an important way for my country to solve the shortage of animal protein, and it will definitely develop greatly in the future.To this end, several issues should be paid attention to in the process of strengthening research: First, there are many types of insects with complex living habits. How to further develop and utilize species with more economic value.The second is to conduct extensive research on feed insect bait and develop feed resources that are low-cost, widely sourced, and suitable for the growth and development of feed insects.5. Effects of black soldier fly larvae meal replacing fish meal on the growth performance, body composition, serum biochemical indicators and antioxidant capacity of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei 1710242274484900.jpg Fish meal is the most important high-quality animal protein raw material for aquatic animals, with high protein content It has the characteristics of high content, balanced amino acids, rich unsaturated fatty acids, no anti-nutritional factors and easy digestion and absorption. It is widely used in carnivorous or omnivorous aquatic animal feeds.With the rapid development of my country's aquaculture industry, the demand for fishmeal has been increasing in recent years. However, long-term overfishing of marine fisheries has led to a shortage of fishery resources. Fishmeal production has been decreasing year by year, and the raw material market has been in short supply, causing prices to continue to rise.The high price of fishmeal has resulted in high feed costs, which has seriously restricted the sustainable development of the aquaculture industry.Therefore, seeking healthy, safe, resource-rich and cheap protein alternative sources has become one of the effective ways to solve the fishmeal shortage problem.The black soldier fly (Hermitiallucens), also known as the bright-spotted water fly, is an insect belonging to the family Diptera. The larval stage can efficiently convert organic matter such as livestock and poultry manure, household food waste, etc. into its own nutrients. It has It has the characteristics of strong fecundity, wide adaptability, large biomass, easy processing and comprehensive nutrition.Black soldier fly larvae meal (BSFLM) is a dry insect meal obtained by screening, drying and crushing the black soldier fly larvae stage. Due to the consumption of waste from different sources, the nutritional content of black soldier fly larvae powder There are certain differences. Generally, the dry matter of insect meal contains 35% to 45% crude protein and 10% to 40% crude fat. The essential amino acid pattern is similar to that of fish meal. It has broad application prospects as animal feed.Studies have shown that black soldier fly larvae powder replaces part of the fish meal in feed, and has achieved good application results in rainbow trout, sea bass, yellow catfish, Jian carp, koi and turbot.Litopenaeus vannamei, also known as White Penaeus vannamei, has the characteristics of fast growth, wide breeding distribution and high nutritional value. It is the shrimp breeding species with the largest breeding area and annual output in the world and in my country.Research shows that the apparent digestibility of black soldier fly larvae powder (crude fat content up to 37.0%) by Litopenaeus vannamei in dry matter and crude protein is both above 82%, and it is found in high salt (30.7‰) Under breeding conditions, black soldier fly larvae meal (crude fat content: 15.1%) can partially replace fish meal without affecting the growth and body composition of Litopenaeus vannamei.Litopenaeus vannamei is an euryhaline species and one of the few shrimp species that can tolerate low salt. Therefore, fishmeal substitutes are added to the feed to study its effects on the growth performance, body composition, and body composition of Litopenaeus vannamei under low-salt conditions. The impact of serum biochemical indicators and antioxidant capacity has practical significance.6. Materials and Methods 6.1 The test feed uses fish meal (crude protein content: 73.7%, crude fat content: 7.9%), soybean meal, and peanut meal as the main protein sources, high-gluten flour as the main sugar source, and fish oil and phospholipid oil as the main fats. Prepare the basal feed (G0, as a control) from the source, and then replace 10% (G10), 15% (G15), 20% (G20), 25% (G25), 30% (G30) of the basal feed with black soldier fly larvae powder. ) is used to prepare 5 kinds of feeds with fish meal. The data analysis chart of the composition and nutritional level of 6 kinds of test feeds is as follows
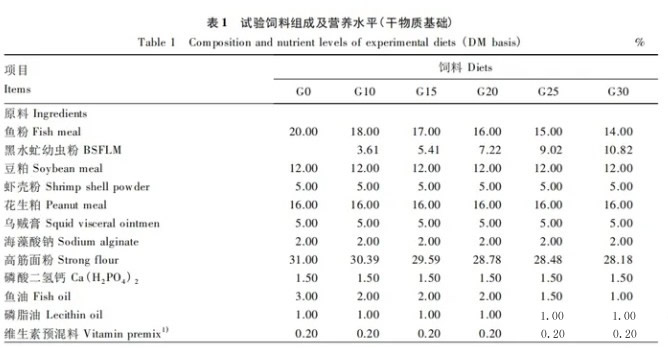
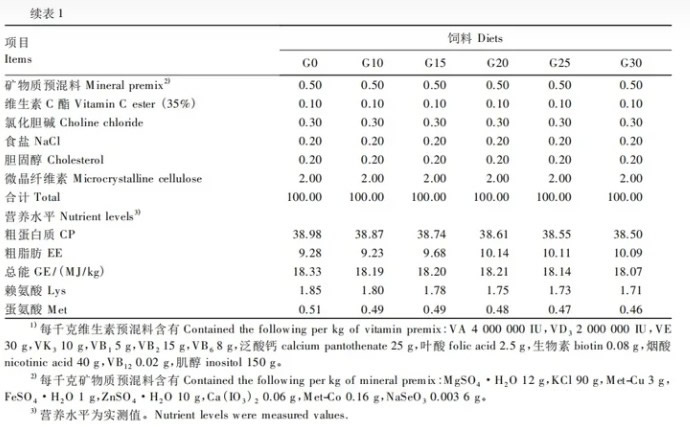
. The feed raw materials are crushed and passed through an 80 mesh sieve. Trace ingredients such as vitamins and minerals are mixed according to the step-by-step expansion method. All raw materials are mixed. After uniformity, add an appropriate amount of water and mix well. Use an SLX-80 twin-screw extruder to make pellet feed with a particle size of 0.5 mm. Dry it at 55°C.
After natural cooling, put it into a sealed bag and store it in a -20°C refrigerator. spare.Black soldier fly larvae powder is provided by Guangzhou Feixite Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The nutritional content is: crude protein 40.85%, crude fat 31.16%, crude ash 13.04%, moisture 3.16%, methionine 0.63%, lysine 2.02%.
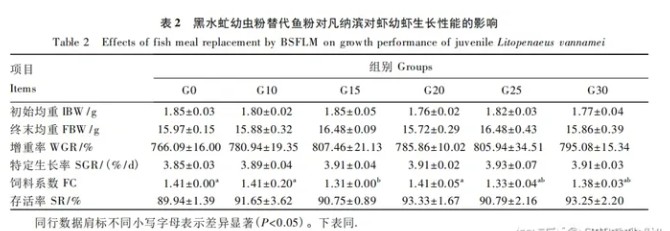
6.2 Results and Analysis 6.2.1 The effect of black soldier fly larvae meal replacing fish meal on the growth performance of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. The data analysis is shown in Table 2 as follows

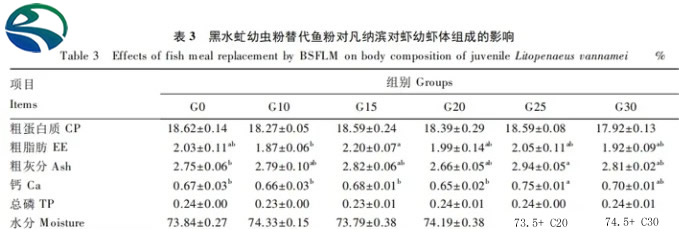
Data Table 2 shows that each substitution group (G10 ~ G30 group ) The terminal average weight, weight gain rate, specific growth rate and survival rate of juvenile shrimp tended to increase compared with the G0 group, but the difference did not reach a significant level (P>0.05).Only the feed coefficient of the G15 group was significantly lower than that of the G0 group (P<0.05), which was 9.29% lower than that of the G0 group. There was no significant difference between the other groups (P>0.05).6.2.2 Effect of replacing fish meal with black soldier fly larvae meal on the body composition of Litopenaeus vannamei larvae 
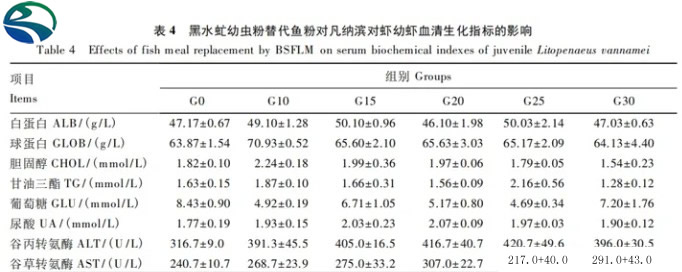
As can be seen from Table 3, there is no significant difference in the crude protein, crude fat, total phosphorus and moisture content of the larvae in each group ( P>0.05); only the crude ash and calcium content of juvenile shrimp in the G25 group were significantly higher than those in the G0 group (P<0.05), and there was no significant difference between the other groups (P>0.05).6.2.3 Effects of black soldier fly larvae meal replacing fish meal on serum biochemical indicators of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei 1710243693106974.jpg As can be seen from Table 4, serum albumin, globulin, cholesterol, There was no significant difference in triglyceride, glucose, urea contents and alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase activities compared with the G0 group (P>0.05).6.2.4 Effect of replacing fish meal with black soldier fly larvae meal on serum antioxidant index of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei
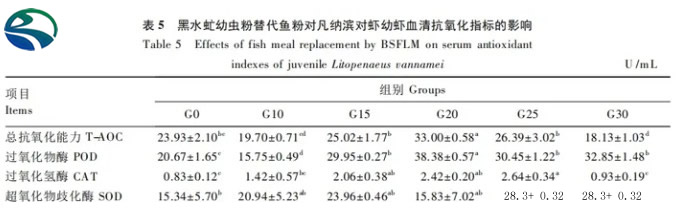
As can be seen from Table 5, compared with the G0 group, the total antioxidant capacity of the serum of juvenile shrimp in the G20 group was significantly increased (P <0.05), the G30 group was significantly reduced (P<0.05); compared with the G0 group, the serum peroxidase activity of juvenile shrimp in the G15~G30 group was significantly increased (P<0.05), and the G10 group was significantly reduced (P<0.05); the serum catalase activity showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of substitution level. The serum catalase activity of juvenile shrimp in the G15~G25 group was significantly higher than that in the G0 group. (P<0.05); the serum superoxide dismutase activity of juvenile shrimp in the G25 group was significantly higher than that in the G0 group (P<0.05), and there was no significant difference between other groups (P>0.05).6.3 Effects of replacing fish meal with black soldier fly larvae meal on the growth performance and body composition of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. The results of this test show that the replacement of black soldier fly larvae meal by 30% (black soldier fly larvae meal addition is 10.82%) or less The fish meal had no significant effect on the final average weight, weight gain rate, specific growth rate and survival rate of juvenile shrimps of Litopenaeus vannamei. The weight gain rate, specific growth rate and survival rate of juvenile shrimps in each substitution group were higher than those of the control. Group (G0 group), the growth performance of juvenile shrimp in the 15% substitution group (black soldier fly larvae powder added is 5.41%) is the best, which is consistent with the experiment of Cummins et al. The fish meal with water fly larvae meal addition amount of 21%) or less has no significant effect on the weight gain rate, specific growth rate, feed coefficient and survival rate of Litopenaeus vannamei. The 20% replacement group (black soldier fly larvae meal addition amount of 7%) is basically the same, but the difference between the two is that this experiment is an alternative study using high-fat black soldier fly larvae meal in low-salinity, low-fishmeal Litopenaeus vannamei juvenile shrimp compound feed. Under this breeding model, it is still feasible for black soldier fly larvae meal to replace fish meal, which once again shows that juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei can make good use of black soldier fly larvae meal.It shows that black soldier fly meal can replace fish meal in an appropriate amount in Litopenaeus vannamei feed, but the amount of substitution is related to the insect species and its nutritional composition.In experimental animals such as carp, koi, turbot, Atlantic salmon, yellow catfish and barramundi, it was concluded that black soldier fly larvae powder can partially replace fish meal, but the replacement amount is different in different experimental animals, and the replacement amount Related to the source of black soldier fly larvae.Research shows that replacing 0 to 100% fish meal with black soldier fly larvae powder and defatted black soldier fly larvae powder has no significant impact on the crude protein, crude fat, crude ash and moisture content of juvenile carp. This is consistent with the results in yellow catfish and Australian catfish. The results are consistent with the results that replacing fish meal with black soldier fly larvae meal has no significant effect on body composition in lungfish.In this experiment, only the 25% substitution group (black soldier fly larvae powder added was 9.02%) had a significant increase in crude ash and calcium contents. There was no significant difference in the body composition of the other substitution groups from the control group. This is because One result is that when black soldier fly larvae powder replaces 40% of fish meal (the black soldier fly larvae powder is added at 14%), the crude fat content of the shrimp body of Litopenaeus vannamei is replaced by 80% (the black soldier fly larvae powder is added at 28%). The reports that fishmeal of or below has no significant effect on the crude protein content of shrimps, and that replacing 100% fishmeal (the amount of black soldier fly worm meal added is 36%) on the crude ash content of shrimp bodies are not completely consistent. This may be due to the black soldier fly larvae powder used in the experiment. The nutritional composition (especially the mineral composition) is related to the difference in the amount of addition, which needs to be studied in depth.6.4 Black soldier fly larvae meal replaced fish meal on juvenile shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. In this trial, black soldier fly larvae meal replaced 30% or less of fish meal on the serum albumin, globulin, cholesterol, triglyceride, glucose, and urea contents of juvenile shrimp. As well as the activities of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, there was no significant impact, indicating that under the conditions of this experiment, black soldier fly larvae powder has no significant effect on juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei.

